

Research
Research Interests
-
Groundwater Use
-
Irrigation
-
Remote Sensing
-
Machine/Deep Learning Applications
-
Water Resources Management
Ongoing
High Spatio-temporal Effective Precipitation Estimation for the Western United States
This study combines remote sensing, machine learning, and data-driven approaches to improve the estimation of effective precipitation for the irrigated croplands of the Western U.S. By incorporating these estimates into groundwater pumping estimations, the approach helps improve irrigation water management and provides valuable insights into groundwater use.


Previous
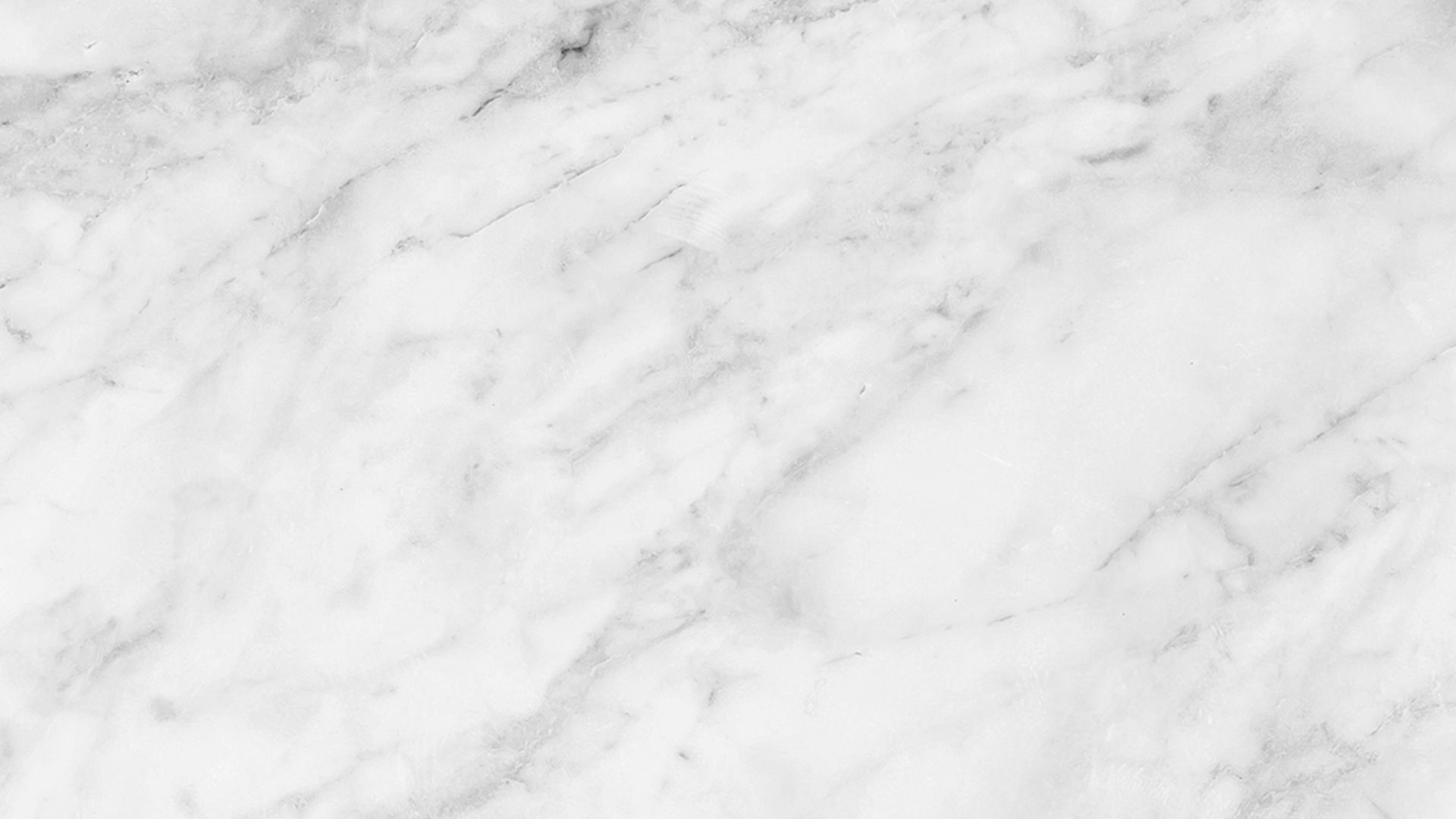
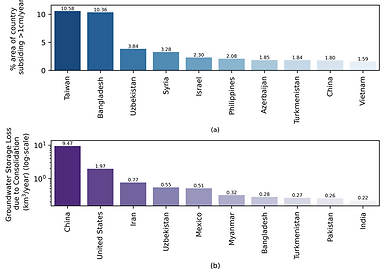
Global Monitoring of Groundwater Extraction Using Automated Assessment of Land Subsidence Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning
Groundwater overextraction causes land subsidence and irreversible storage loss. This study integrates remote sensing and machine learning to predict global subsidence at ~2 km resolution, estimating an annual groundwater storage loss of 17 km³ due to aquifer consolidation. Approximately 73% of subsidence is concentrated in cropland and urban regions, emphasizing the critical need for sustainable groundwater management in these areas.

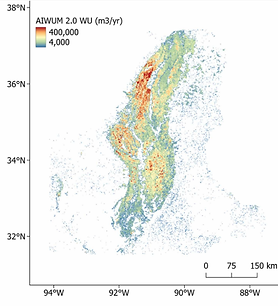
Improving crop-specific groundwater use estimation in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain
We use remote sensing and machine learning to improve a groundwater use model developed by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). By applying a Distributed Random Forests algorithm, we predict annual and monthly groundwater use (2014–2020) across the Mississippi Delta at 1-km resolution, using data from existing flowmeters. Our model outperforms the USGS model, achieving a higher R² (0.51 vs. 0.42) and lower errors (RMSE: 0.14 m, MAE: 0.09 m). This improves our ability to predict groundwater use in areas with limited data.
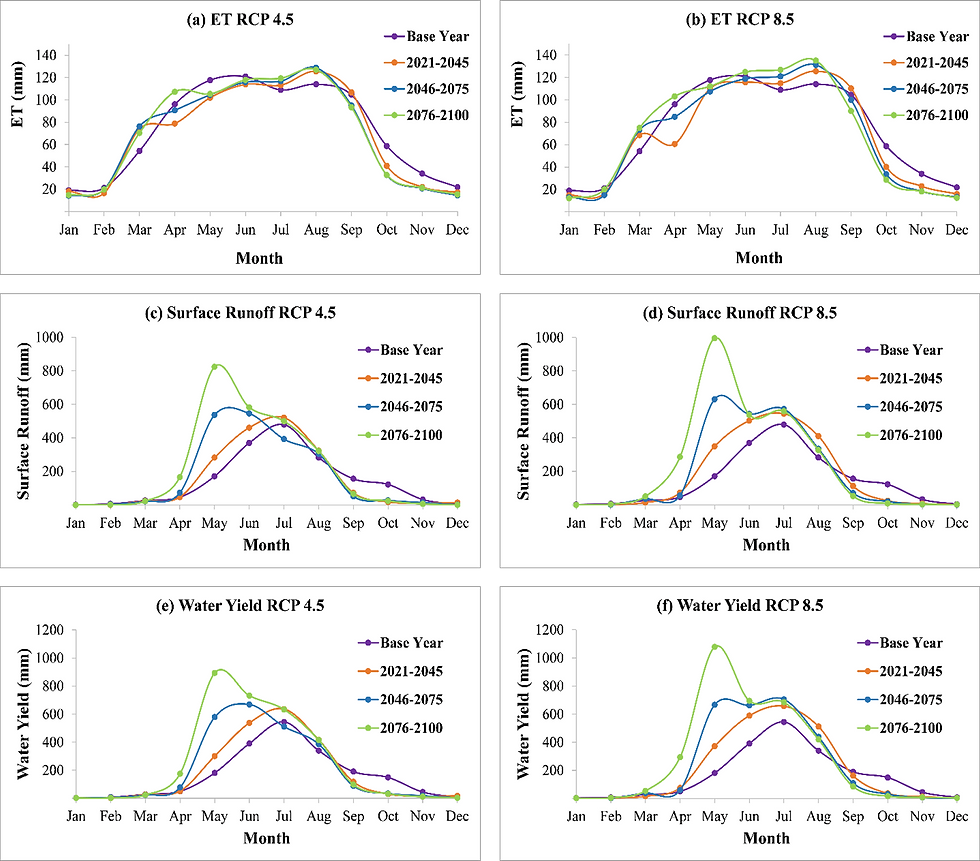
Modeling Climate Change Impact on Hydrology of Halda River Basin using Soil & Water Assessment Tool (SWAT)
Halda River is of tremendous importance in Bangladesh being the country's main natural fish spawning ground. With proximity to the sea, Halda River is the major tributary to the tidal river Karnaphuli, thereby, very prone to future climate change impacts. Also, growth of nearby Chittagong city may impact the land use pattern of Halda River Basin. In this study, impact of climate change on flow and hydrologic components of Halda River was studied using Soil & Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Model.



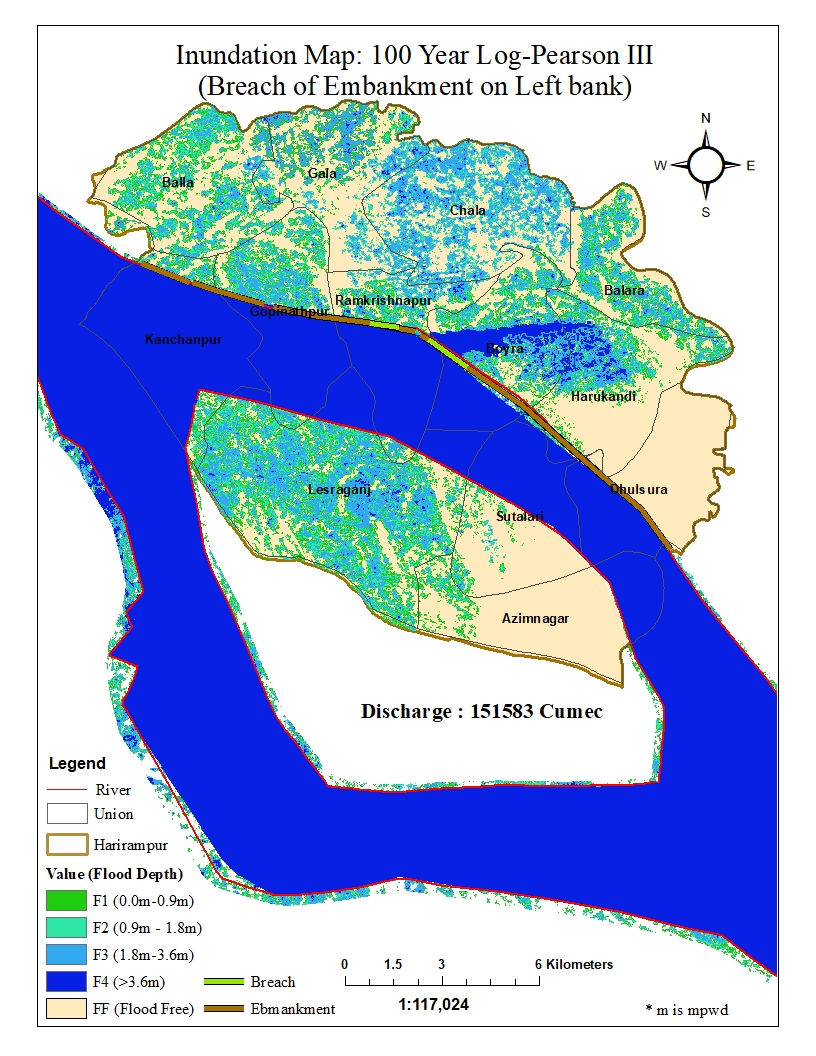
Flood Inundation Modeling with HEC-RAS and Hazard mapping
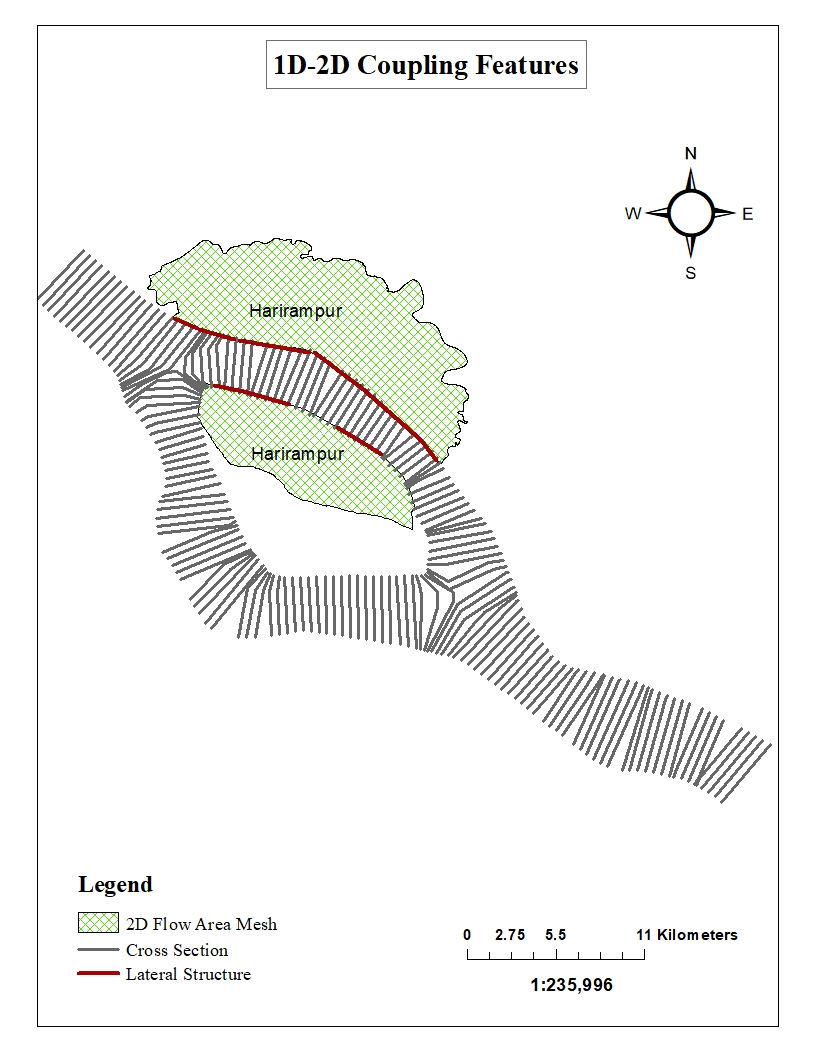
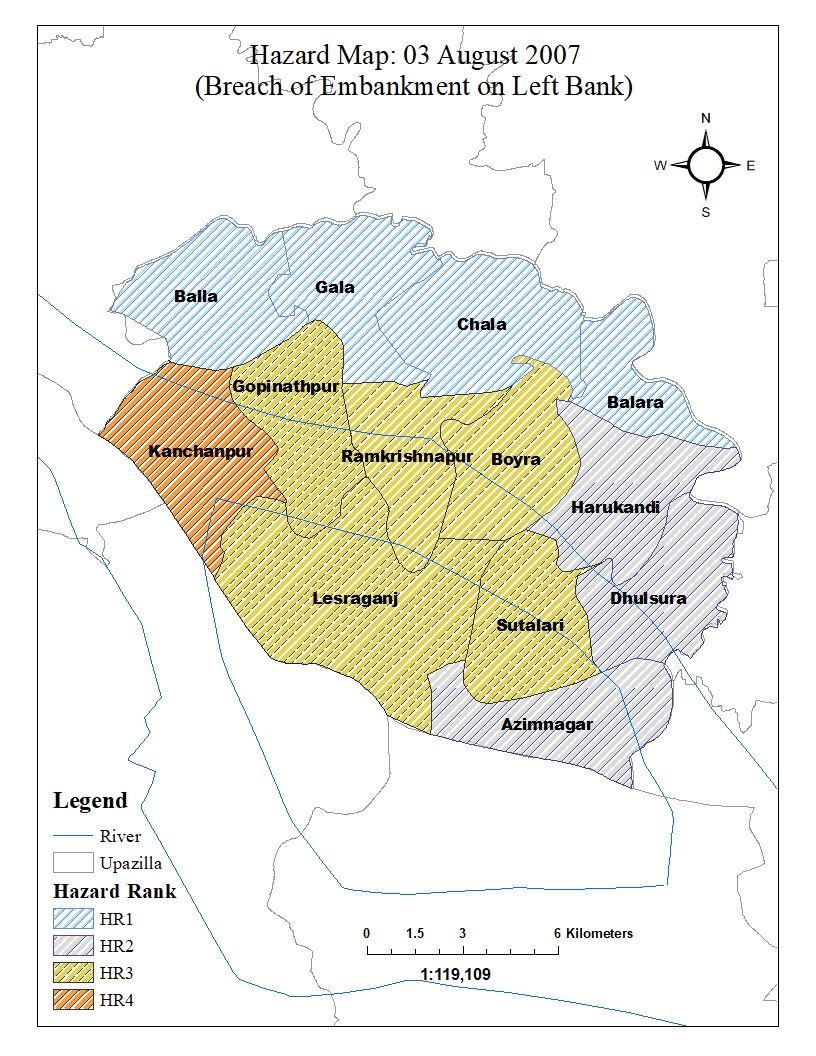
A coupled 1-D and 2-D HEC-RAS model was developed to generate a flood inundation map for the Harirampur region along the left bank of the Padma river. Harirampur is a very vulnerable region with recurrent flood events in the monsoon season. The model was developed for four scenarios- inundation i) without embankment ii) with proposed embankment iii) over-topping of embankment & iv) breaching of embankment. The output flood maps were validated with historic flood inundation maps. Also, flood inundation for 100 Year Flow (Log-Pearson III) was analyzed for each of the scenarios. Finally, flood hazard maps were developed for the scenarios to identify the most sensitive areas (Union scale) to flood damage.

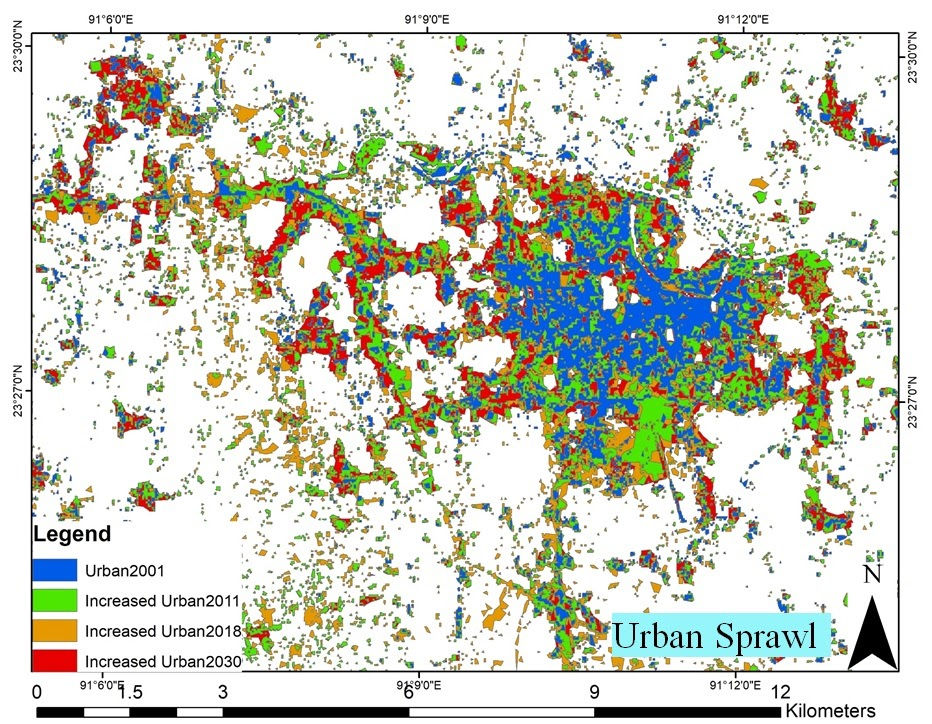
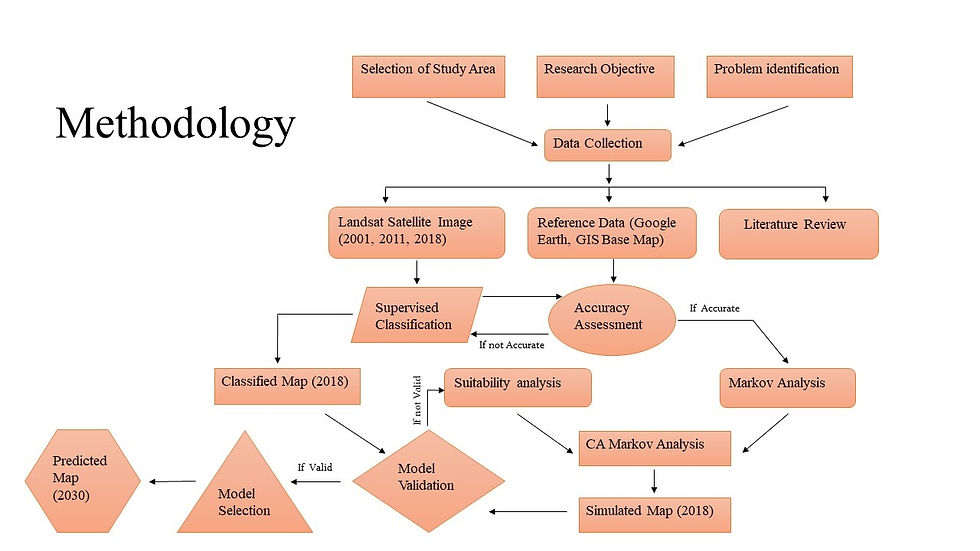
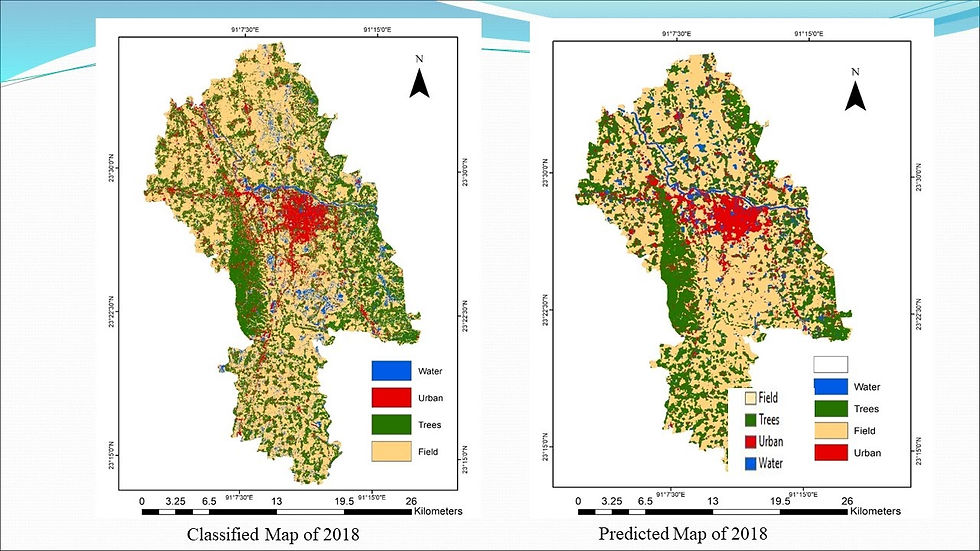
Land Use Change Prediction of Cumilla City
The objectives of this research were to develop a land-use prediction model and analyze the future urban growth of Cumilla, a major city in Bangladesh. For the study, ArcGIS was used as a data processing and Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE) analysis tool, and mathematical modules like Markov and Cellular Automata Markov (CA Markov) were run on IDRISI platform. Three major components of the land use prediction model were 1) Markov analysis; 2) MCE; and 3) CA Markov analysis. Analyses show significant growth of urban areas in 2030. Results also showed a decrease in percentage of agricultural lands and trees, while percentage of waterbody was almost the same.

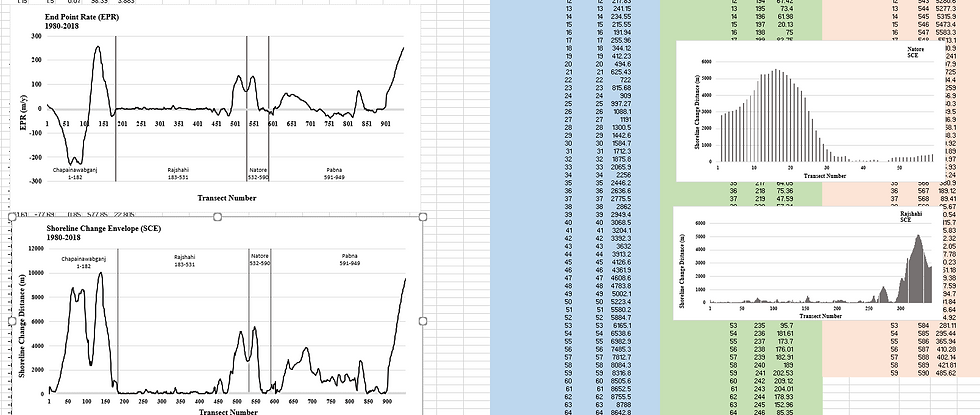
Trend Analysis of Shoreline Changes of the Ganges River
The Ganges basin, extending from Tibet to the coast of the Bay of Bengal, is one of the largest river basins of Asia and a significant part of it lies in Bangladesh. The temporal change along the left bank of the Ganges river, flowing through the North West region of the country, was the focus of this study. Landsat images from 1980-2018 along with Google Earth historical imagery were used to delineate approximately 230 km shoreline. Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS), an ArcGIS extension, was used to analyze the historic trend of shoreline change. DSAS estimates parameters such as Shoreline Change Envelope (SCE) and End Point Rate (EPR) to determine shoreline change rate. Analyses showed that most of the erosion occurred from 1980 to 2000 while in 1990-200 and 2010-2018 accretion was dominant.



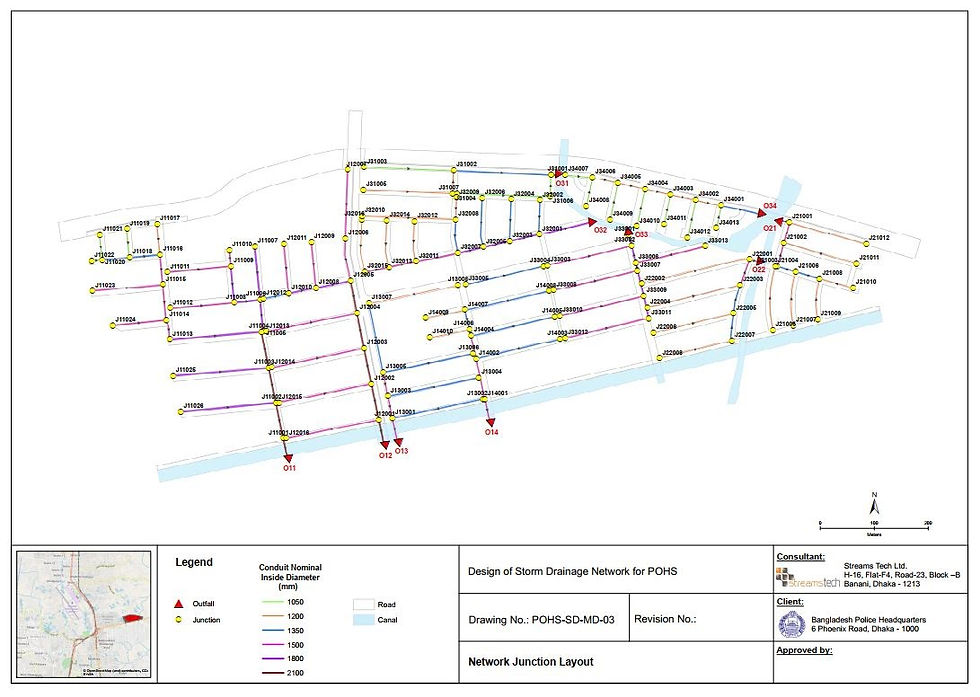
Design of Storm Drainage Network
Designing a storm drainage network for a major housing project while working for Streams Tech Ltd. Project responsibility included layout design of the network in GIS, hydrologic and hydraulic design along with network efficiency analysis in SWMM, mapping and report writing.



Design of Water Supply Network
Designing a water supply network for a major housing project while working for Streams Tech Ltd. Project responsibility included layout design, hydraulic design along with network performance analysis in EPANET, mapping and report writing.




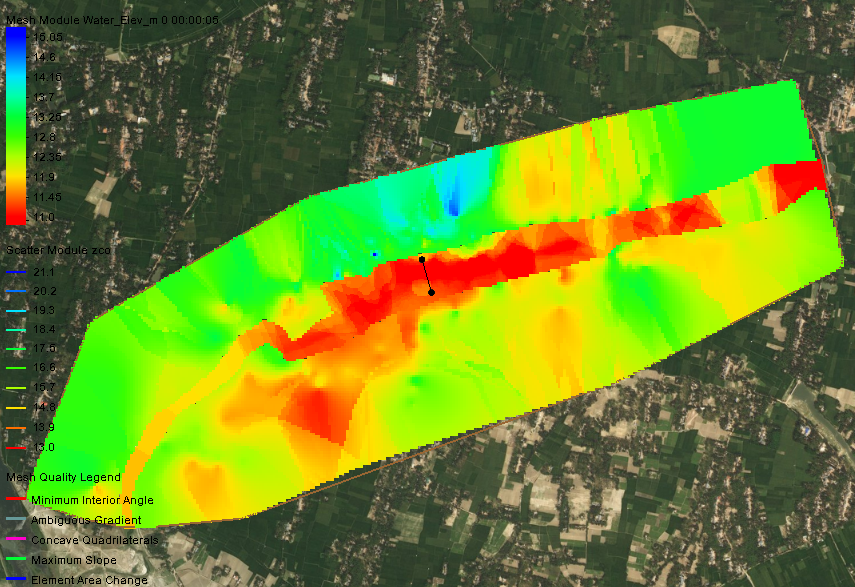
Hydrodynamic Modeling for Bridge Project
As part of the Streams Tech Ltd. team, major responsibilities were to perform hydraulic parameters analysis without and with bridge condition, sediment transport and scour analysis, morphological analysis of the river reaches using HECRAS.



Performance Evaluation of Zero Liquid Discharge-Effluent Treatment Plants (ZLD- ETPs) in Textile Industries of Bangladesh
A project undertaken by Department of Environment of Government of Bangladesh, which was awarded to Center for Environmental and Resource Management (CERM), BUET. The objective of the project was to determine the efficiency at which textile industries of Bangladesh were performing in terms of liquid waste management.
Market Sounding Study of 40-Story Commercial Complex for Chittagong Port Authority (CPA)
A market-sounding study to determine the feasibility of a 40-Story commercial building planned for Chittagong Port Authority (CPA). As part of the BUET team, responsibilities were to conduct survey on the real estate market, compare similar development works by other port authorities with CPA’s plan, analyzing the environmental, structural and traffic feasibility studies of the proposed project, and maintain liaison between CPA and BUET.
Recycling Potential of Textile Solid Waste
In Bangladesh, while prioritizing the disposal and management of textile liquid wastes, the necessity of management of textile solid wastes (TSWs) is often neglected. In this context, an attempt was made in this study to find a sustainable disposal option for TSW. This research focused on a particular type of solid waste, very dusty in composition, generated in slitting, brushing and sueding machine in dyeing units of the composite textile industries. Using this particular type of TSW, papermaking was attempted following manual procedures. TSW at different ratios was added to scrap abandoned paper mixture to produce handmade papers. A pulp consistency test and different tests on produced paper e.g. basis weight, bulk, and density, book bulk, thickness, hygroexpansivity, formation, moisture, and finish were conducted according to the Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry (TAPPI) methods. ISO standards were followed to determine the quality of pulp and type of papers. The result was promising and showed a high potential for the use of TSW in the papermaking industry.